In modern smart lighting and security systems, sensing technology plays a crucial role. Among the most widely used are PIR (Passive Infrared) and microwave sensors, each with its unique advantages, disadvantages, and application scenarios. Understanding the differences between these two sensing technologies is vital for selecting the right products. This article will delve into the principles, advantages, disadvantages, and suitable applications of PIR and microwave sensors.
1.Working Principles
PIR Sensors: PIR sensors utilize passive infrared technology to detect changes in infrared radiation in their environment. When a person or animal enters the detection range of the sensor, the infrared radiation generated by their body heat triggers the sensor to activate. PIR sensors require no external power supply to operate and typically send a signal to lighting devices or security systems.
Microwave Sensors: In contrast, microwave sensing technology uses high-frequency microwave signals to detect object movement. Microwave sensors emit microwave signals and receive the signals reflected back from surrounding objects. When an object (such as a person or vehicle) enters the detection area, its movement alters the reflected signal, thereby activating the sensor.

2.Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of PIR Sensors:
Low Power Consumption: As passive devices, PIR sensors usually exhibit low power usage.
Privacy Protection: PIR sensors only detect infrared radiation and do not capture images, thus effectively protecting user privacy.
Wide Applicability: They are commonly used in both indoor and outdoor lighting control and security systems.
Disadvantages of PIR Sensors:
Limited Detection Range: The detection range of PIR sensors is typically smaller and can be affected by environmental factors (e.g., temperature, wind).
Sensitivity to Motion: PIR sensors respond more slowly to stationary objects, which can be a drawback in applications where someone remains in the detection area for an extended period.
Advantages of Microwave Sensors:
Wide Detection Range: Microwave sensors generally have a larger detection area and greater adaptability.
High Sensitivity: They can detect minute movements, making them suitable for dynamic environments.
Strong Penetration: Microwave signals can penetrate non-metal objects, reducing the likelihood of obstructions affecting performance.
Disadvantages of Microwave Sensors:
Higher Power Consumption: Compared to PIR sensors, microwave sensors typically consume more power, especially when continuously emitting microwaves.
Higher False Alarm Rate: Due to their sensitivity to all moving objects, microwave sensors may have a higher false alarm rate, potentially triggered by small animals.
Potential Privacy Issues: Microwave sensors might track the motion of objects, raising concerns about user privacy.
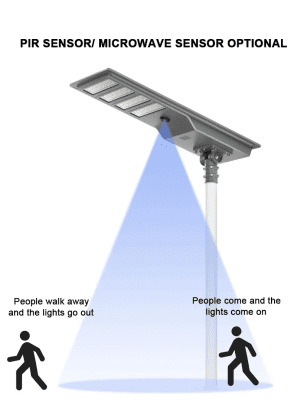
3.Suitable Scenarios
PIR Sensors: Particularly well-suited for residential and office environments where lighting control and intrusion monitoring are needed. Their sensitivity to body heat makes them ideal for automatically turning lights on and off or for security monitoring.
Microwave Sensors: More appropriate for larger spaces, such as warehouses, parking lots, and shopping malls. Their extensive detection range and high sensitivity allow them to function effectively in dynamic environments.
Understanding the characteristics of PIR and microwave sensors is crucial when selecting the right sensing device. PIR sensors are ideal for environments that prioritize low energy consumption and privacy protection, while microwave sensors are better suited for areas requiring extensive detection capabilities and high sensitivity. By choosing the appropriate sensing technology based on specific needs, users can enhance system efficiency and security, driving advancements in the smart lighting and security market.